


2K
A common abbreviation for the year 2000, sometimes "Y2K" when
referring to Year 2000 date conflicts in computer operation. "K"
stands for thousands.
accumulator method
Procedure for adding the closest census tracts to an unfinished district. Tracts
are added until the population of the district is within the gross variance
allowed by the average district population.
Jump: Accumulator Animation, Seed
Tract, The Method
apportionment
The distribution of population among a fixed set of geographic areas. States are
apportioned seats in the House of Representatives based on the decennial census.
Commonly refers to any of the subsequent methods used to district a state for
the selection of any electoral representatives.
Jump: The History
census block
Subset of a census tract created for the convenience of tabulation and to
provide more specific demographic information on the population. Tracts may
include many or no BNA blocks.
census code
The Census Bureau refers to each tract and block by a string of codes. The state
code (06 for California) is followed by the county code (58 different codes for
California in alphabetic sequence), the tract code (one to three digits,
depending on historic assignment) and, where appropriate, a decimal block code
(two digits) for various subdivisions and counting conveniences of the census.
The resulting code might, for example, be 06118001.02 for an individual block.
census tract
A definite area of occupied land or water area. The Census Bureau maintains
boundaries of populated areas which may be adjusted each decade to maintain an
approximate count of 5-10,000 persons. Blocks are frequently created within high
population tracts to better organize the counting process. When they are
changed, tracts are usually subdivided among existing blocks rather than being
re-arranged.
 centroid
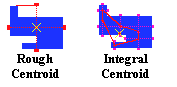
centroid
Geometric center point of an object. Referring to the moving center of the
accumulated district boundaries, as distinct from the center point of the
original or subsequent tracts. A rough centroid is the simple average distance
between the north/south and east/west boundaries. A more accurate, but
unnecessary, centroid may be determined from the integration of all opposing
points in a shape.
Jump: Centroid Animation, Accumulator Method
commuity of interest
Common districting factor, usually suggesting that cities and counties be
maintained whole in any district line drawing. Often vaguely cited, but rarely
defined, this element is not included in the Fair Vote 2K Intiative. Commentary:
Fair Vote Factor?
 compact
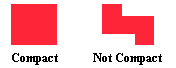
compact
Having the smallest perimeter. Two districts may have the same area but
irregular objects will have a longer perimeter than more regular (square or
round) objects. Tracts are predefined by the Census Bureau and tend to follow
irregular geographic or county boundaries. The Centroid Proximate method ensures
that the district will have the fewest irregularities, and thus be more compact.
Jump: Geometric Criteria
 contiguous
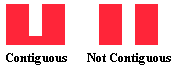
contiguous
Adjacent or next in order. Contiguity does not ensure compactness or proximity,
only that the all the areas of a district are connected. Two large tracts
connected by a small strand of lengthy highway, a bridge or river course would
still be contiguous, but not compact.
Jump: Geometric Criteria
debasement
Any legislative act which reduces electoral strength. Gerrymandering favors one
group of electors, debasing the political strength of all others.
Jump: Districting Principles
decennial census
Population count required by the constitution every ten years, completed by the
end of the first year of each decade.
Jump: Census Apportionment
deferential
Granting a special favor to one individual or group over others.
Jump: Districting Principles
demographic
Describing the various characteristics of a specific population. The Census
Bureau acquires dozens of individual, racial, residential and commercial factors
during its count.
Jump: Ethocentric Criteria
dilution
Reduction or diminution of a factor. Gerrymandering can reduce the electoral
impact of certain electors by packing or fracturing their population.
Jump: Supreme Court
distance measurement
Formula for calculating mileage distances between any two points on earth. Basic
method of accumulating the closest tracts in the formation of an electoral
district.
Refer: Computer Programming
Jump: Accumulator Animation, Seed
Tract
district type
Sets of district for a specific legislative function. Districts for seats in the
US House or Representatives are different than the districts for the California
State Assembly. The Initiative proposes nesting Assembly districts to form two
other types of district: State Senate and the Board of Equalization.
Jump: Initiative Draft, Nesting
Method
districting
Process of revising district boundaries in order to balance the population
represented by individual members of a district type. Jump: Districting Practice
Equal Protection Clause
Provision of the Fourteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution which requires
"equal protection under the law". Precludes individuals or groups from
being treated differently by the law.
Link: US
Constitution, 14th Amendment
Refer: Court Rulings
Jump: Supreme Court
ethnocentric
Relating to racial characteristics. Districting which
intends or results in disadvantages to specific racial groups is
unconstitutional. Jump: Supreme Court
ethocentric
Relating to the ethos or interests of any group. Districting based on
"compelling state interests" is constitutional, but cannot override
other stipulated factors. Jump: Ethocentric
Criteria
fracturing
Method of dividing an electoral group into multiple districts to reduce their
electoral influence. Ant: packing
gerrymander
Bizarre and grossly disfigured districts named after the salamander shapes
created by Eldridge Gerry in Massachusetts. The process of selecting boundaries
for political objectives.
Jump: Districting History, Gerry's Gallery
gross variance
The difference between the district with the largest population and the smallest
population. May be expressed as a percentage of the average population. The
Initiative allows a gross variance of up to one percent for each district type.
Jump: Initiative Draft
nesting method
Procedure for grouping existing districts of one type to create districts of
another type. Used in the 1990 census to create State Senate districts from
pairs of State Assembly districts. The Initiative also proposes nesting sets of
twenty State Assembly districts to create districts for the Board of
Equalization.
Jump: Initiative Draft, Nesting
Method
packing
Method of batching an electoral group into a single district to reduce their
electoral influence.
Ant: fracturing
policentric
Considerations based on any variety of combination of political interests.
Gen: policentric
Jump: Policentric Criteria
preferential
Granting a unique benefit to an individual or group. Gerrymandering gives a
preference to one group of electors over all others.
 proximate
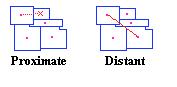
proximate
Closest or nearest object. Referring to the tract center that is the least
direct distance away from the district centroid. More definitive than adjacent
or next in order by reference to the northwest-southwest scan line, used to
select the starting tract for the next district compilation. Distance between
the centroid and the center points of adjacent tracts can be determined by a
simple longtitude/latitude measurement.
Jump: Accumulator Animation, Seed
Tract, Accumulator Method
residual tract
Isolated population areas left unassigned if the seed scan does not conform with
the state boundaries.
seed scan
Method of selecting the first census tract which will begin the accumulation of
population for a district. For the state of California, a Northwest to Southeast
scan avoids residual tracts.
Jump: Scan Animation
seed tract
First census tract selected during the seed scan, which becomes the foundation
for subsequent accumulation of additional tracts in the formation of a district.
Jump: District Seed
| Home | Law | Schedule | Campaign |
Info@FairVote2K.Org